Detection and Defense
- Protect and Limit Domain Admins
- Isolate administrative workstations
- Secure local administrators
- Time bound and just enough administration
- Isolate administrators in a separate forest and breach containment using Tiers and ESAE
Protect and Limit Domain Admins
- Reduce the number of Domain Admins in your environment.
- Do not allow or limit login of DAs to any other machine other than the Domain Controllers. If logins to some servers is necessary, do not allow other administrators to login to that machine.
- (Try to) Never run a service with a DA. Credential theft protections which we are going to discuss soon are rendered useless in case of a service account.
Set Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated for DAs.
Protected Users Group
Protected Users is a group introduced in Server 2012 R2 for better protection against credential theft by not caching credentials in insecure ways. A user added to this group has following major device protections:
- Cannot use CredSSP and WDigest - No more cleartext credentials caching.
- NTLM hash is not cached.
- Kerberos does not use DES or RC4 keys. No caching of clear text cred or long term keys.
If the domain functional level is Server 2012 R2, following DC protections are available:
- No NTLM authentication.
- No DES or RC4 keys in Kerberos pre-auth.
- No delegation (constrained or unconstrained)
-
No renewal of TGT beyond initial four hour lifetime - Hardcoded, unconfigurable Maximum lifetime for user ticket and Maximum lifetime for user ticket renewal
- Needs all domain control to be at least Server 2008 or later (because AES keys).
- Not recommended by MS to add DAs and EAs to this group without testing “the potential impact” of lock out.
- No cached logon ie.e no offline sign-on.
- Having computer and service accounts in this group is useless as their credentials will always be present on the host machine.
Isolate administrative workstations
Privileged Administrative Workstations (PAWs)
- A hardened workstation for performing sensitive tasks like administration of domain controllers, cloud infrastructure, sensitive business functions etc.
- Can provides protection from phishing attacks, OS vulnerabilities, credential replay attacks.
- Admin Jump servers to be accessed only from a PAW, multiple strategies
- Separate privilege and hardware for administrative and normal tasks.
- Having a VM on a PAW for user tasks.
Secure local administrators
LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution)
- Centralized storage of passwords in AD with periodic randomizing where read permissions are access controlled.
- Computer objects have two new attributes - ms-mcs-AdmPwd attribute stores the clear text password and ms-mcs-AdmPwdExpirationTime controls the password change.
- Storage in clear text, transmission is encrypted.
[Note] With careful enumeration, it is possible to retrieve which users can access the clear text password providing a list of attractive targets
Time Bound Administration - JIT
Just In Time (JIT) administration provides the ability to grant time-bound administrative access on per-request bases.
Check out Temporary Group Membership! (Requires Privileged Access Management Feature to be enabled which can’t be turned off later)
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins' -Members newDA -MemberTimeToLive (New-TimeSpan -Minutes 60)
Time Bound Administration - JEA
JEA (Just Enough Administration) provides role based access control for PowerShell based remote delegated administration.
- With JEA non-admin users can connect remotely to machines for doing specific administrative tasks.
- For example, we can control the command a user can run and even restrict parameters which can be used.
- JEA endpoints have PowerShell transcription and logging enabled.
Detection and Defense - Tier Model
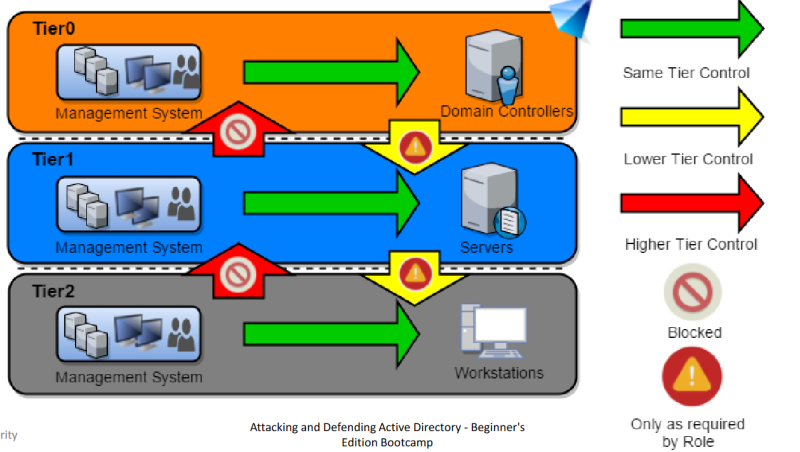
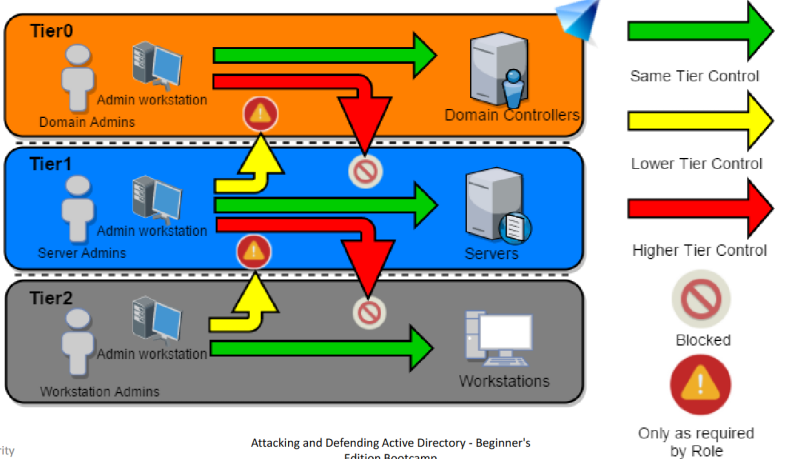
Active Directory Administrative Tier Model
Composed of three levels only for administrative accounts:
- Tier 0 - Accounts, Groups and computers which have privileges across the enterprise like domain controllers, domain admins, enterprise admins.
- Tier 1 - Accounts, Groups and computers which have access to resources having significant amount of business value. A common example role is server administrators who maintain these operating systems with the ability to impact all enterprise services.
- Tier 2 - Administrator accounts which have administrative control of a significant amount of business value that is hosted on user workstations and devices. Examples include Help Desk and computer support administrators because they can impact the integrity of almost any user data.
Control Restrictions - What admins control. Logon Restrictions - Where admins can log-on to.
Tier Model : Control Restrictions
Tier Model : Logon Restrictions
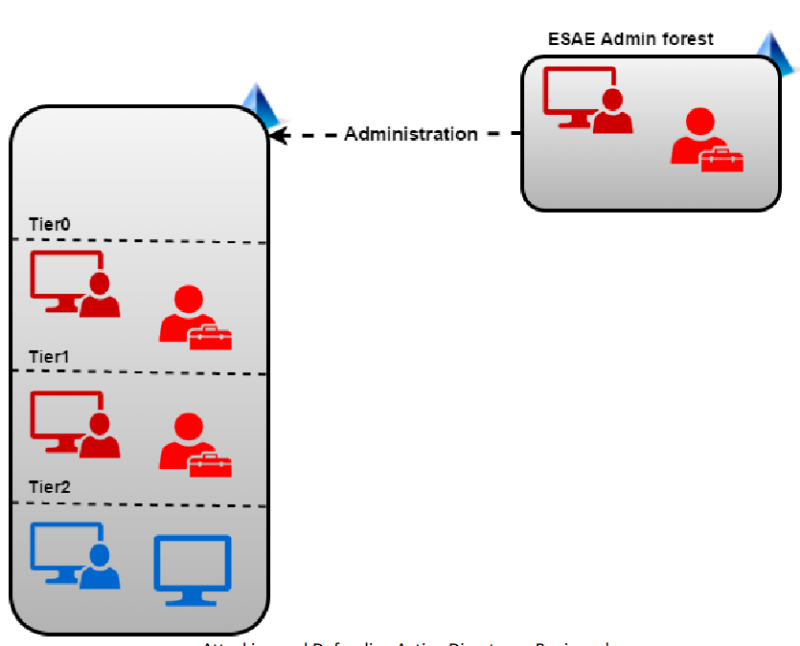
ESAE
ESAE (Enhanced Security Admin Environment)
- Dedicated administrative forest for managing critical assets like administrative users, groups and computers.
- Since a forest is considered a security boundary rather than a domain, this model provides enhanced security controls.
- The administrative forest is also called the Red Forest.
- Administrative users in a production forest are used as standard non-privileged users in the administrative forest.
- Selective Authentication to the Red Forest enables stricter security controls on logon of users from non-administrative forests.
Microsoft retired ESAE in 2021 and replaced it with Privileged Access Strategy but it is still worth discussing
Credential Guard
It uses virtualization-based security to isolate secrets so that only privileges system software can access them.
Effective in stopping PTH and Over-PTH attacks by restricting access to NTLM hashes and TGTs. It is not possible to write Kerberos tickets to memory even if we have credentials.
Windows Credential Guard Documentation
- But, credentials for local accounts in SAM and Service account credentials from LSA Secrets are NOT protected.
- Credential Guard cannot be enabled on a domain controller as it breaks authentication there.
- Only available on the Windows 10 Enterprise edition and Server 2016.
- Mimikatz can bypass it but still, no need to not use it.
Device Guard (WDAC)
It is a group of features designed to harden a system against malware attacks. Its focus is preventing malicious code from running by ensuring only known good code can run
Three primary components:
- Configurable Code Integrity (CCI) - Configure only trusted code to run
- Virtual Secure Mode Protected Code Integirty - Enforces CCI with Kernerl Mode (KMCI) and User Mode (UMCI)
- Platform and UEFI Secure Boot - Ensures boot binaries and firmware integrity
Introduction to Device Guard, Virtualization-Based Security, and Code Integrity Policies
- UMCI is something which interferes with most of the lateral movement attacks we have seen.
- While it depends on the deployment (discussing which will be too lengthy), many well known application whitelisting bypasses - signed binaries like csc.exe, MSBuild.exe etc. - are useful for bypassing UMCI as well.
Check out the LOLBAS project:
MDI
..identify, detect, and investigate advanced threats, compromised identities, and malicious insider actions directed at your organization.
- MDI sensors are installed on DCs and Federation servers. Analysis and alerting is done in the Azure cloud.
MDI can be used for detecting:
- Recon
- Compromised credentials (Brute-Force, Kerberoasting etc.)
- Lateral movement (PTH, OPTH etc.)
- Domain Dominance (DCSync, Golden ticket, Skeleton key etc.)
- Exfiltration
MDI Bypass
The key is to avoid talking to the DC as long as possible and make appear the traffic we generate as attacker normal.
- To bypass DCSync detection, go for users which are whitelisted. For example, the user account used for PHS may be whitelisted.
- Also, if we have NTLM hash of a DC, we can extract NTLM hashes of any machine account using netsync
- If we forge a Golden Ticket with SID History of the Domain Controllers group and Enterprise Domain Controllers Group, there are less chances of detection by MDI
C:\AD\Tools\BetterSafetyKatz.exe "kerberos::golden /user:dcorp-dc$ /domain:dollarcorp.moneycorp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-1874506631-3219952063-538504511 /groups:516 /sids:S-1-5-21-280534878-1496970234-700767426-516,S-1-5-9 /krbtgt:4e9815869d2090ccfca61c1fe0d23986 /ptt" "exit"
Defense - Golden Ticket
Some important Event ID
Event ID:
- 4624: Account Logon
- 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
Defense - Silver Ticket
Some important Event ID
Event ID:
- 4624: Account Logon
- 4634: Account Logoff
- 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
Defense - Skeleton Key
Events:
- System Event ID 7045 - A service was installed in the system. (Type Kernel Mode driver)
Events (Audit privilege use must be enabled):
- Security Event ID 4673 - Sensitive Privilege Use
- Event ID 4611 - A trusted logon process has been registered with the Local Security Authority
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"}
Not recommended:
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*" -and $_.message -like "*mimidrv*"}
Mitigation:
- Running lsass.exe as a protected process is really handy as it forces an attacker to load a kernel mode driver.
- Make sure that you test it thoroughly as many drivers and plugins may not load with the protection.
New-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name RunAsPPL -Value 1 -Verbose
# Verify after a reboot
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=12} | ?{$_.message -like "*protected process*"}
Defense - DSRM
Events:
- Event ID 4657 - Audit creation/change of HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DsrmAdminLogonBehavior
Defense - Malicious SSP
Events:
- Event ID 4657 - Audit creation/change of HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\SecurityPackages
Defense - Kerberoast
Events:
- Security Event ID 4769 - A Kerberos ticket was requested
Mitigation:
- Service Account Passwords should be hard to guess (greater than 35 characters)
- Use Group Managed Service Accounts (Automatic change of password periodically and delegated SPN Management)
Since 4769 is logged very frequently on a DC. We may like to filter results based on the following information from logs:
- Service name should not be krbtgt
- Service name does not end with $ (to filter out machine accounts used for services)
- Account name should not be machine@domain (to filter out requests from machines)
- Failure code is '0x0' (to filter out failures, 0x0 is success)
- Most importantly, ticket encryption type is 0x17
Defense - Unconstrained Delegation
Mitigation:
- Limit DA/Admin logins to specific servers
- Set "Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated" for privileged accounts.
Security Focus: Analyzing “Account is sensitive and cannot be delegated” for Privileged Accounts
Defense - ACL Attacks
Events:
- Security Event ID 4662 (Audit Policy for object must be enabled) - An operation was performed on an object
- Security Event ID 5136 (Audit Policy for object must be enabled) - A directory service object was modified
- Security Event ID 4670 (Audit Policy for object must be enabled) - Permissions on an object were changed
Useful tool:
- AD ACL Scanner - Create and compare create reports of ACLs.
Defense - Trust Tickets
SID Filtering
- Avoid attacks which abuse SID history attribute (child to root domain privilege escalation, that is, DA from a Child to EA on forest root).
- Enabled by default on all inter-forest trusts. Intra-forest trusts are assumed secured by default (MS considers forest and not the domain to be a security boundary).
- But, since SID filtering has potential to break applications and user access, it is often disabled.
Selective Authentication:
In an inter-forest trust, if Selective Authentication is configured, users between the trusts will not be automatically authenticated. Individual access to domains and servers in the trusting domain/forest should be given.
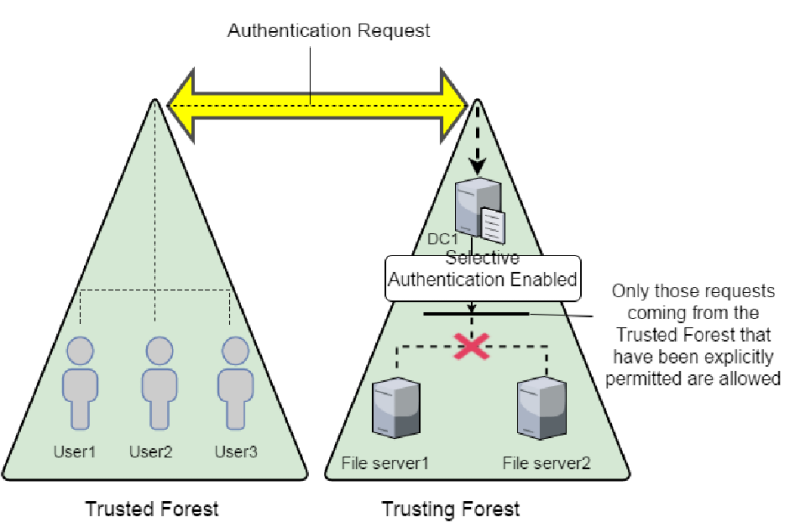
Defense - Deception
Deception is a very effective technique in active directory defense.
- By using decoy domain objects, defenders can trick adversaries to follow a particular attack path which increases chances of detection and increase their cost in terms of time.
- Traditionally, deception has been limited to leave honey credentials on some boxes and check their usage but we can use it effectively during other phases of an attack
What to target? Adversary mindset of going for the lowest hanging fruit and illusive superiority over defenders.
We must provide the adversaries what they are looking for. For example, what adversaries look for in a user object:
- A user with high privileges.
- Permissions over other objects.
- Poorly configured ACLs.
- Misconfigured/dangerous user attributes and so on.
Let’s create some user objects which can be used for deceiving adversaries. We can use Deploy-Deception for this: https://github.com/samratashok/Deploy-Deception
[Note] Windows Settings / Security Settings / Advanced Audit Policy Configuration / DS Access / Audit Directory Service Access Group Policy needs to be configured to enable 4662 logging
User Deception
Creates a decoy user whose password never expires and a 4662 is logged whenever x500uniqueIdentifier - d07da11f-8a3d-42b6-b0aa-76c962be719a property of the user is read:
Create-DecoyUser -UserFirstName user -UserLastName manager -Password Pass@123 | Deploy-UserDeception -UserFlag PasswordNeverExpires -GUID d07da11f-8a3d-42b6-b0aa-76c962be719a -Verbose
This property is not read by net.exe, WMI classes (like Win32_UserAccount) and ActiveDirectory module. But LDAP based tools like PowerView and ADExplorer trigger the logging
Create a decoy user named decda and make it a member of the Domain Admins group. As a protection against potential abuse, Deny logon to the user on any machine.
Create-DecoyUser -UserFirstName dec -UserLastName da -Password Pass@123 | Deploy-PrivilegedUserDeception -Technique DomainAdminsMemebership -Protection DenyLogon -Verbose
If there is any attempt to use the user credentials (password or hashes) a 4768 is logged. Any enumeration which reads DACL or all properties for the user will result in a 4662 logging.
Recommended Readings
Securing Privileged Access:
Securing Privileged Access Documentation
Best Practices for Securing Active Directory: